
The European Union is a partnership of 27 European countries, covering a large part of the European continent. The EU is home to about 447 million people, or almost 6% of the world's population. Citizens of EU countries are also EU citizens.
Ukraine also intends to develop relations with the European Union, in particular to become a full member of the bloc.
However, the EU has faced many challenges in recent years, such as the 2008 global financial crisis, the influx of migrants from Africa and the Middle East, Brexit and the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Currently watching
Now a full-scale war between Russia and Ukraine has been added to the challenges, since it was to the EU countries that several million Ukrainian refugees fled from the war. And many European countries supply us with weapons, ammunition or finance priority social needs.
ICTV Facts has prepared a detailed analysis of how the European Union works, what institutions it has and what they are responsible for.
When was the European Union created
After World War II, in the 50s, European countries began to talk about uniting for economic growth and future protection of the world. The Treaty on the European Union was signed on February 7, 1992 in Maastricht, the Netherlands. The Maastricht Treaty came into force on November 1, 1993.
The EU received its current structure and powers in 2007 under the Lisbon Treaty, also known as the Reform Treaty. According to these documents, the bloc's 27 members agreed to pool their sovereignty and delegate many powers to the EU.
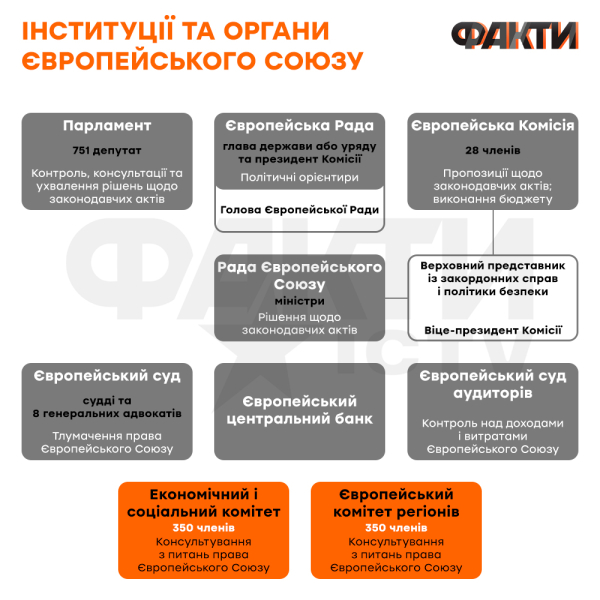
Main EU institutions
The EU has seven main institutions, which can be roughly grouped according to their executive, legislative, judicial and financial functions. The EU also has dozens of smaller bodies that make laws, coordinate foreign policy and trade, and manage the overall budget.
Want to rest? Come to Facti.GAMES!
The European Council , the EU's group of top political leaders, consists of the president or prime minister of each member state. At council meetings, the general direction of EU development is determined and pressing high-level issues are resolved. EU members elect a president who can serve up to two terms of 2.5 years. The current president is former Belgian Prime Minister Charles Michel .
The European Commission is the main executive body of the EU. It proposes legislation, manages the budget, implements decisions, issues regulations and represents the EU around the world at summits, negotiations and international organizations. Commission members are appointed by the European Council and approved by the European Parliament. The commission is now headed by former German Defense Minister Ursula von der Leyen .
The European Parliament is directly elected and its representatives are appointed by the population of each member state. The EP does not propose bills, but laws cannot be adopted without the approval of European parliamentarians. The European Parliament also negotiates and approves the EU budget and oversees the activities of the commission. Parliament is currently headed by Maltese politician Roberta Metsola .
The Council of the European Union – or Council of Ministers – is the second legislative branch of government and is also involved in the adoption of laws. The Council consists of government ministers from all EU member countries. Ministers meet in groups according to their areas of activity: foreign ministers meet in one group, agriculture ministers in another, and so on.
The Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) is the EU's highest judicial body, which interprets the bloc's legislation for national courts and resolves disputes. The CJEU consists of the European Court of Justice (decides on violations by member states, interprets legislation) and the General Court – there is a wide range of consideration of claims against EU institutions.
The European Central Bank (ECB) manages the euro for the 19 countries that use this currency and regulates the EU banking system. The director of the ECB is the former head of the International Monetary Fund, Christine Lagarde .
The European Court of Auditors (ECA) audits the EU budget, checks how funds are spent and reports cases of fraud to Parliament, the Commission and national governments.
The offices of the above-mentioned institutions are located throughout the EU with headquarters in Brussels, Frankfurt, Luxembourg and Strasbourg.
Powers of the European Parliament
Although the European Parliament cannot initiate bills, laws for the EU cannot be passed without parliamentary approval. It discusses all laws, including budgetary ones, with the commission and the Council of Ministers under a procedure known as co-decision-making.
International agreements, in particular trade agreements, also require the approval of the European Parliament. The President of the EP, who is elected by this body, must also sign laws for their final adoption.
The European Parliament confirms the members of the European Commission and can also force the commission to resign. Although this has never happened before, the commission resigned en masse in 1999 due to a corruption scandal.
Elections to the European Parliament
Direct elections to the European Parliament are held in all member countries of the European Union. Each country has its own quota of deputies, which is calculated depending on the population. The territory of the European Union is divided into electoral districts, each of which covers the territory of only one state.
In each state, deputies are elected according to national rules, so the quota of members of the European Parliament can be distributed differently within the country and divided into several electoral districts.
Currently, Belgium, Ireland, Italy, Poland and France have more than one constituency. In other states, the boundaries coincide with the boundaries of a single district.
The European Parliament consists of 751 members. But only 720 are chosen because seats became available after Britain left the EU. Now these seats are kept in parliament in case of expansion.
How Ukraine can change the forces in the European Parliament
Poland has 51 members in the European Parliament; Germany – 96; France – 74; Italy -73; Czech Republic – 21 deputies; Baltic countries – only 25 deputies. Ukraine also plans to become a member of the EU and then will have to elect its deputies to the EP.
In a commentary to Facts ICTV , Candidate of Political Sciences, Associate Professor at Kiev National University. T. Shevchenko Igor Reiterovich noted that in this case, a union of countries such as Poland, Ukraine, and the Czech Republic could be created in the European Parliament. The accession of the Baltic countries is also possible.
Poland many years ago, even before its membership, said that the so-called young Europe could have a large cell of deputies who would influence the agenda in the European Parliament. Despite the fact that there are large factions in the EP that unite various political parties in different directions – liberals, democrats, socialists, etc. – then the principle of state positioning will work for parliamentarians. That is, MEPs will focus on bills that are important for their country. Therefore, in general, deputies from different countries can unite in coalitions, for example, the majority of Central-Eastern Europe.
According to Igor Reiterovich, the representation of Ukraine in the European Parliament can strengthen the coalition of Slavic countries and will have a significant influence on making decisions that we and our neighbors need.
— That is, in general, this could lead to a revolution in taking into account the positions of the countries that were the last to join the EU. For example, Poles complain that they are listened to less and that they do not have the influence they would like. But Ukraine’s accession could change the situation greatly,” the political scientist noted.
The expert also noted that today the European Parliament has informal leadership from three countries – Germany, France and Italy. They are leaders because these are the richest countries of the European Union, they are the engines of the EU economy and these countries have the most deputies in the European Parliament.
They attract representatives of other countries of old Europe, for example, the Benelux countries (Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg) and then have the opportunity to pass key bills.
By the way, some Polish political forces, for example, Jaroslaw Kaczynski’s Law and Justice, speculated on this during the elections. They said that if Donald Tusk (Civic Platform) becomes Prime Minister of Poland, he will carry out the tasks of Berlin and Poland will turn into Germany.
— That is, you can see that the Poles are attracted by this dominance. But it is worth noting that this dominance has a completely objective character, because the population in Germany, France and Italy is much larger, and therefore the representation in the European Parliament is greater. But with Ukraine’s accession to the EU, this dominance may change quite seriously,” notes Igor Reiterovich.
For some countries of old Europe this may be a certain risk, but they take it calmly. Maybe they hope that they will win the Ukrainians over to their side.
What does the European Commission do?
The commission consists of 27 commissioners, one from each member state, and is headed by the president. The President is elected by the European Council and confirmed by the European Parliament after each parliamentary election, and leads the commission for a five-year term.
The Board of Commissioners includes:
- EU High Representative for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy;
- the Trade Commissioner, who leads trade negotiations;
- the Competition Commissioner, responsible for bloc-wide corporate regulation;
and 23 other commissioners who focus on energy, jobs and growth, climate and financial regulation.
The Commission is responsible for drafting legislation, drawing up and distributing the EU budget, and implementing EU laws.
How the EU carries out its foreign policy
The Common Foreign and Security Policy concerns diplomacy, security and defense cooperation. Leadership at the highest level is exercised by the national governments of the bloc's member countries through the European Council and the Council of Ministers.
Foreign policy is carried out by the EU High Representative for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy. This position is also known as the EU Foreign Minister. It is currently occupied by Spanish politician Josep Borrell.
It is worth noting that the EU played a leading role in negotiations on the Paris climate agreement and the Iran nuclear agreement, which were concluded in 2015. In 2016, the European Union entered into an agreement with Turkey to limit the intake of refugees.
The EU imposed sanctions against the Russian Federation after the annexation of Crimea in 2014. However, before the Russian-Ukrainian war broke out in 2022, members of the bloc debated how closely to cooperate with Moscow in energy and other areas, given the EU's dependence on Russian oil and gas.
But with the outbreak of Russia’s war against Ukraine in 2022, Germany stopped the large-scale Russian gas pipeline project Nord Stream 2, and the EU in general increased sanctions against Russian financial institutions and individuals, and Putin in particular.
Does the European Union have its own army?
EU countries cooperate in military missions on a voluntary basis. However, there is no standing EU army independent of the armies of member states. By the way, the countries' membership in the EU and the NATO military bloc partially coincides. In September, President Volodymyr Zelensky said Ukraine had signed an application to join NATO on an accelerated basis.
The Lisbon Treaty recognizes NATO as Europe's primary means of collective defense.
EU budget
European Union spending in 2020 (the last year for which the European Commission has published full accounts) amounted to more than $197 billion.
About 35% goes to agriculture, in particular to payments to farmers, the development of fisheries, forestry, and rural communities.
Money is also allocated for economic, social and territorial cohesion to help less developed EU countries. About 14% of the budget goes to the research and development, energy, transport and telecommunications sectors.
The EU budget is reviewed annually.
Schengen Area
The Schengen area includes countries that have agreed to abolish all border controls among themselves and strengthen law enforcement cooperation.
The zone includes: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Greece, Spain, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Germany, Portugal, Sweden, Italy, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, Malta, Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Slovenia, Hungary, Croatia, as well as Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Norway, Iceland (the last four countries are not EU members).
Other EU institutions
The European Stability Mechanism (ESM) is an EU agency that provides emergency loans directly to governments or private banks in difficulty.
The European Investment Bank (EIB), founded in 1958, is the official investment bank of the EU, providing low-cost loans, equity investments and other financing to thousands of businesses, government programs and the like.
The European Economic Area (EEA) is a 1994 agreement that extends the EU's single market to three non-EU countries: Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway. These three countries, plus Switzerland, form the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), a separate free trade area.
Ukraine – EU
Our state borders with four EU members: Hungary, Poland, Slovakia and Romania.
On March 5, 2007, Ukraine and the EU began the negotiation process on a new agreement. On September 9, 2008, at the Paris Summit, Ukraine and the European Union agreed to conclude an Association Agreement.
The political part of the Association Agreement was signed on March 21, 2014, the economic part on June 27, 2014. On September 16, 2014, the Verkhovna Rada and the European Parliament simultaneously ratified the Association Agreement. It came into force on September 1, 2017.
On February 28, 2022, Ukraine submitted an application for membership in the European Union. On 17 June 2022, the European Commission recommended that the European Council grant Ukraine candidate status. At the same time, official Brussels put forward seven demands for reforms in Ukraine.
On June 23, 2022, the European Council granted Ukraine candidate status for accession to the European Union.
Interesting facts about the EU
- The European Union has 24 official languages.
- The euro currency is used by 19 out of 27 countries.
- The EU slogan is Unity in diversity.
- Germany, with about 83 million inhabitants, is the largest EU country by population, while Malta, with a population of 500 thousand, is the smallest.
- In 2004, eight Central and Eastern European countries joined the EU: the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Slovakia, Slovenia and Estonia.
- The UK left the EU in 2020.
- Currently, the candidate countries for EU membership are Ukraine, Albania, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Serbia, Turkey, and potential candidates are Bosnia and Herzegovina and Kosovo.

