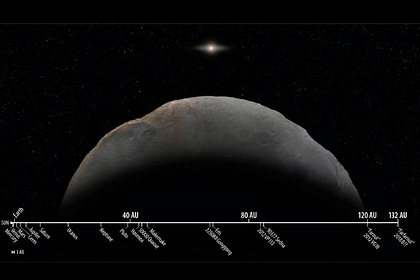
A group of astronomers have confirmed the existence of the planetoid Farfarut, which is four times farther from the Sun than Pluto, making it the most distant object in the solar system known. This was reported in a press release Phys.org.
Farfarut, or 2018 AG37, was discovered in 2018 using the Subaru telescope in Hawaii, but only now scientists have collected enough information to determine its orbit. The orbit parameters were determined from the data obtained by the Gemini North and Magellan telescopes. The average distance to the object is 132 astronomical units (one AU is equal to the distance from the Sun to the Earth – approx. “Lenta.ru” ). At the same time, Farfarut moves in a very elongated orbit, moving as far as possible from the Sun by 175 AU. and approaching it at 27 AU, which is closer to the orbit of Neptune.
The period of revolution around the Sun in the planetoid is about a thousand years, which is explained by the gravitational influence of Neptune since the appearance of the Solar system. Researchers estimate that it reaches 400 kilometers across, which puts it at the lower edge of dwarf planets, assuming that this object is rich in ice.
From the orbit of Farfarut, it is impossible to determine whether there is an unknown massive planet at the edge of the solar system, since the dynamics of the planetoid is too dependent on Neptune. Only those objects that are far from Neptune's gravitational influence can be used to search for planet X, for example, Sedna and 2012 VP113.

