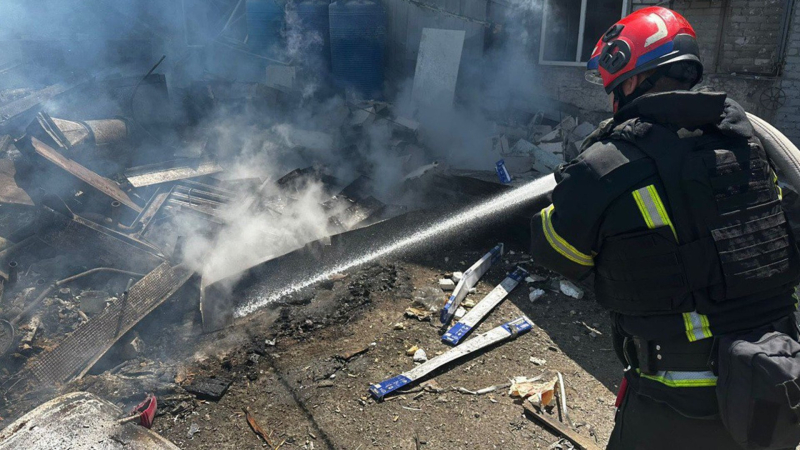
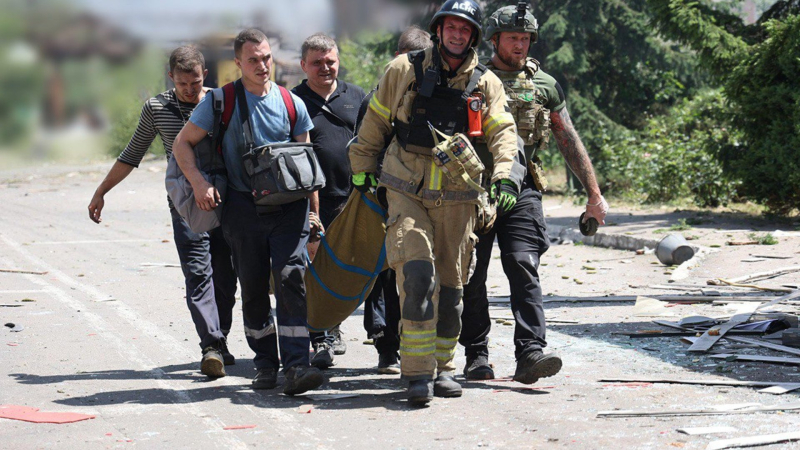
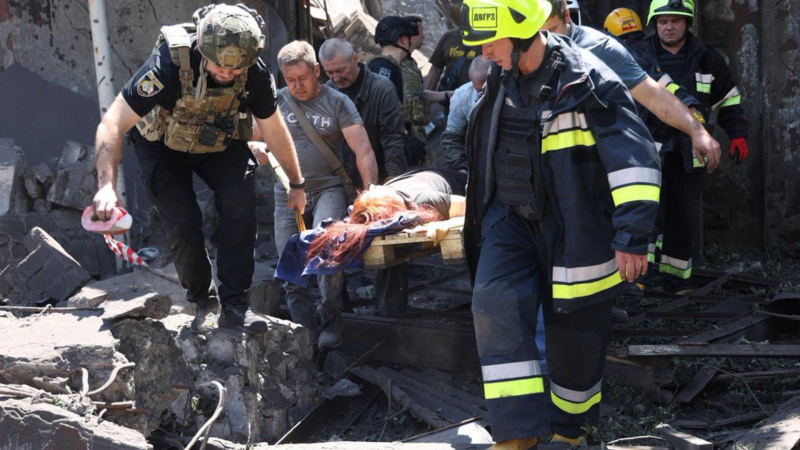
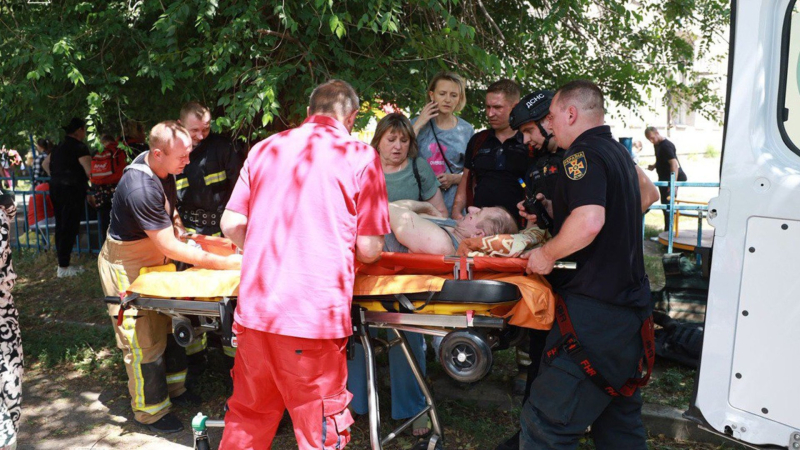
news

Iran is a state isolated from the West, but at the same time extremely active in the region. Despite its isolation and sanctions, the Islamic Republic does not stand aside from geopolitics.
It actively interferes in the affairs of its neighbors, supports various forces and advances its own interests. Over the past decades, the country has formed a complex system of alliances and feuds.
Read our article about Iran's allies and enemies in the Middle East.
Now watching
Which countries are Iran's allies?
Iran’s allies are not only countries, but also powerful non-state groups. Among state partners, Syria should be mentioned first, where the Bashar al-Assad regime has survived thanks to massive support from Tehran – military, financial and technical.
In Iraq, Iranian influence is growing due to support for Shiites who receive resources from Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps.
Outside the region, Iran maintains close ties with Russia, through cooperation in Syria, military supplies, and political convergence amid conflicts with the West.
China is another partner of Iran with which it has long-term economic and energy agreements.
Their relationship is based on mutual benefit:
- Iran needs support in isolation;
- China is interested in stable access to energy resources and influence in the Middle East.
Tehran also cooperates with countries that are themselves under sanctions, such as North Korea and Venezuela, exchanging oil products and technology with them.
Iran's non-state allies include the powerful Shiite organization Hezbollah in Lebanon, which is effectively Tehran's military and political arm in the region. In Yemen, Iran supports the Houthi rebels.
Iran operates through the concept of asymmetric influence – lacking a classically powerful military, it expands its influence through proxy groups, political alliances, religious ties and economic diplomacy.
Some of its allies are situational, or based on shared hostility to the West, Saudi Arabia or Israel , rather than long-term strategic objectives. But the system, despite its complexity, provides Iran with a stable presence in several key locations in the region, from Lebanon to Yemen.
Which countries have neutral relations with Iran
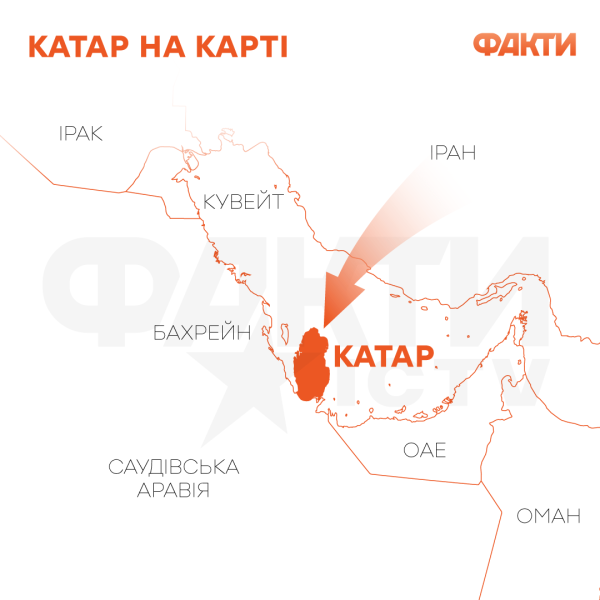
Qatar, despite its status as a US ally, has begun to cooperate more actively with Iran after the diplomatic blockade in 2017, especially in the energy sector. Although the country maintains neutrality.
South Pars is the world's largest gas field, shared by Iran and Qatar in the Persian Gulf.
Therefore, both countries are forced to cooperate in the energy sector, although sometimes competition arises.
Infographics our website
Oman has traditionally remained neutral but maintains stable relations with Iran and often acts as a mediator between it and the West.
Iran's Enemies: Who is the Country at War with?
At the same time, Iran has numerous adversaries. The most prominent of these is Israel, which views Iran as its main existential threat, due to its constant threats, funding of anti-Israel groups, and potential nuclear ambitions.
List of Iran's main enemies:
- Israel
- Saudi Arabia
- USA
Saudi Arabia is Iran’s main regional rival, vying for influence in Yemen, Lebanon and even Syria. Other Gulf states, the UAE and Bahrain, closely coordinate with Saudi Arabia and often oppose Iranian influence.
Saudi Arabia is the main Sunni center of Islam. Iran is the main Shiite state. Both countries see themselves as defenders of the “correct” version of Islam, and this historical religious rivalry increases political tensions.
The United States has remained Iran's main strategic adversary since the 1979 Islamic Revolution, steadily tightening sanctions and building coalitions against Iranian expansion.


























